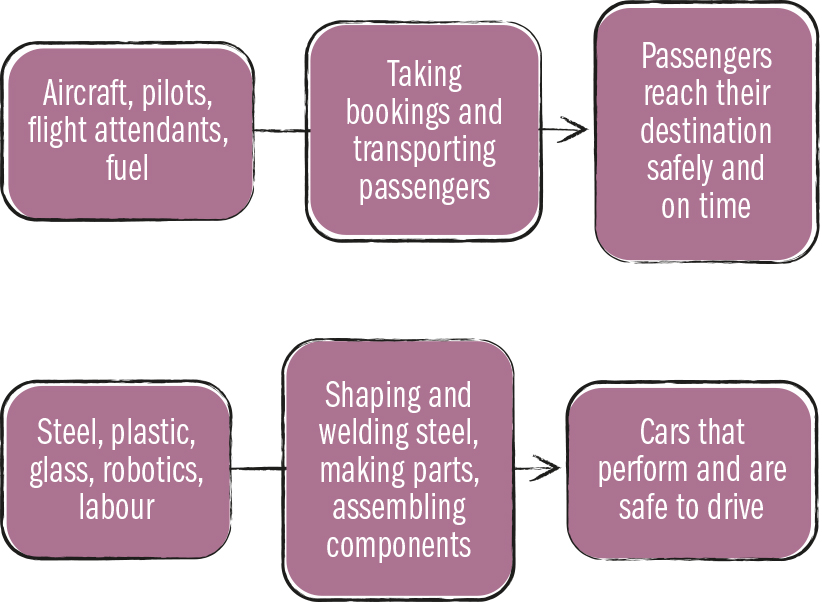
3.1 Introduction
Operations processes are the activities involved in the transformation of inputs into outputs. These may also be referred to as the production system or operations system. Each activity adds value so that the output has a greater value than the cost of inputs. The outputs will be sold for a profit.
Key questions that must be answered are:
- What production activities are required?
- What will be the sequence of the activities?
- How often will the process need to be changed or adjusted?
- What technology will be used?
The operations manager has a role in every part of the operations process. Their goals are to produce goods and provide services which are right the first time, to cut costs by eliminating delays and improving delivery times, produce in a dependable and flexible manner and, finally, control input costs. When assessing the performance of the operations function, the manager will determine how effectively the business makes and assembles raw materials and components into finished goods and services; how quickly it distributes to wholesalers, retailers and customers; and the quality of after-sales customer service.